
The SMEC series evaporative condensers are designed with an efficient counterflow modular structure, ensuring high-performance heat dissipation in demanding cooling applications. Under standard operating conditions, they provide heat dissipation from 200KW to 5000KW, making them suitable for large-scale refrigeration needs.
Key Features:
- Counterflow Modular Design: Optimized for efficient heat exchange and maximum cooling performance.
- Wide Cooling Capacity: Supports 200KW to 5000KW heat dissipation.
- Robust Construction:
- Z-700 (G235) hot-dip galvanized steel sheet casing for corrosion resistance.
- Aviation-grade aluminum alloy ventilation fan for reliable and efficient airflow.
- Integral hot-dip galvanized elliptical steel coil for enhanced heat transfer efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency: Modular design minimizes energy consumption while maximizing performance.
- Low Maintenance: Durable components ensure long service life with minimal upkeep.
Applications:
The SMEC series evaporative condensers are ideal for:
- Large-scale commercial and industrial refrigeration systems.
- Cooling for large-scale data centers.
- Heavy-duty cooling applications requiring high thermal efficiency.
With its modular structure, high cooling capacity, and durable design, the SMEC series evaporative condensers offer an efficient and reliable solution for industrial and commercial cooling demands.
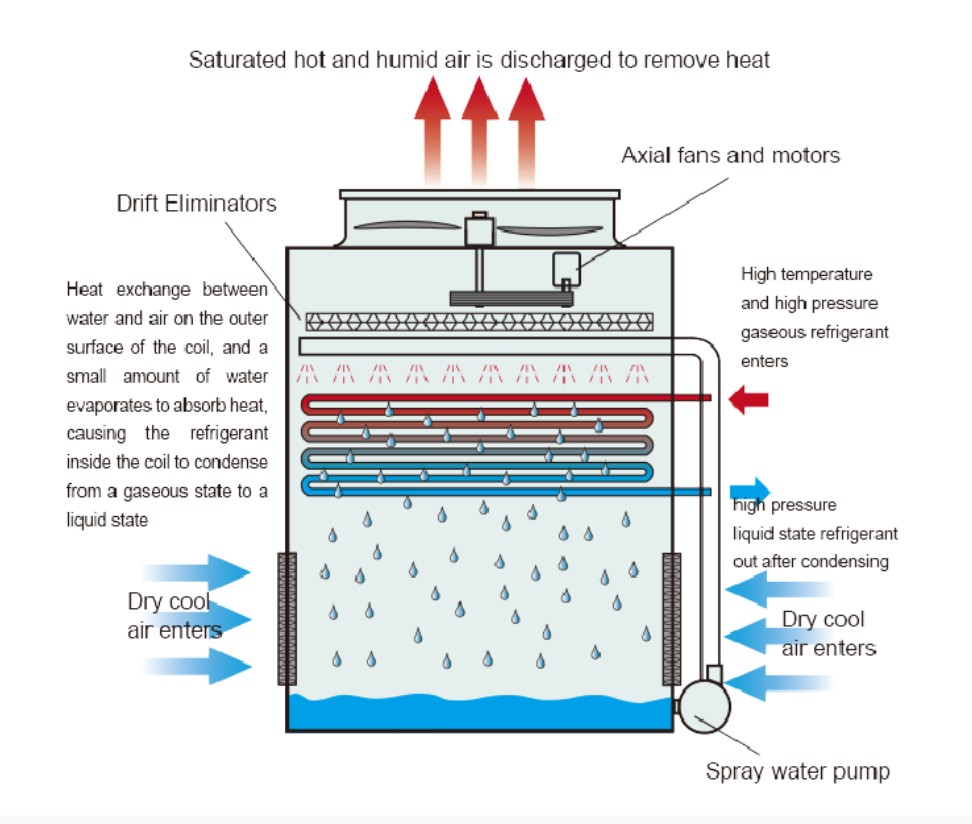
The high-temperature and high-pressure gaseous refrigerant working fluid from the refrigeration compressor enters the inside of the serpentine heat exchange coil from the side of the evaporative condenser, while the external water in the water pan of the evaporative condenser is evenly sprayed onto the surface of the serpentine heat exchange coil through the bottom water pump and upper spray system: The axial flow fan located at the top of the cooling tower draws the surrounding dry and cold air into the interior of the cooling tower. The dry and cold air enters through the lower air intake grille and flows from bottom to top onto the surface of the serpentine heat exchange coil. where it undergoes counter current heat exchange with the external water on the surface of the serpentine heat exchange coil: A small amount of water evaporates into the air to take away heat. condensing the high-temperature and high-pressure gaseous refrigerant working fluid inside the coil. The humid and hot air is discharged by the axial flow fan at the top of the cooling tower, and the condensed liquid refrigerant flows to the storage tank or evaporator.
